Understanding dog behavior is essential for any pet owner or dog enthusiast.
Dogs are complex creatures with their own unique ways of communicating and interacting with the world around them.
By expanding our knowledge of their behavior, we can strengthen our bond with them and foster a healthier, happier relationship.
The Basics of Canine Behavior
Dogs are social animals by nature, originating from pack-hunting ancestors.
Their behaviors often reflect this background, and they communicate through a combination of vocalizations, body language, and facial expressions.
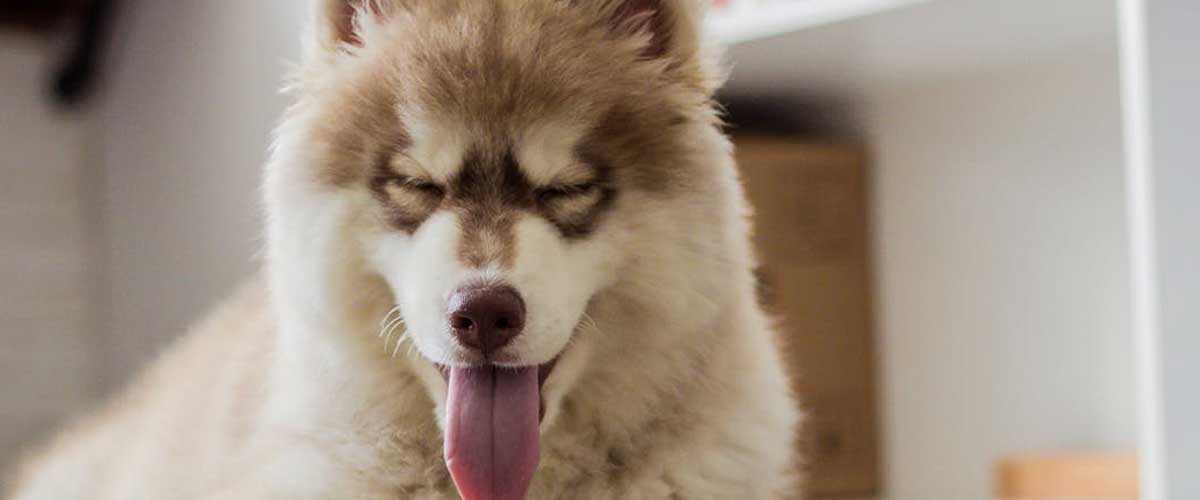
For instance, a wagging tail can signify excitement or happiness, while a lowered tail may indicate fear or submission.
Body Language
To truly understand your dog, it’s vital to pay attention to their body language:
Ears:
Pinned back ears can signal fear or aggression, while perky ears indicate curiosity or engagement.
Eyes:
Direct eye contact can be a sign of confidence or challenge, whereas a soft gaze often indicates calmness.
Posture:
A relaxed stance suggests a comfortable dog, while a tense body can indicate stress or anxiety.
Vocalizations
Dogs use vocalizations such as barking, whining, and growling to express their feelings.
Understanding the context in which these sounds are made helps in deciphering their meaning.
For example, a high-pitched bark might signify play, while growling can be a warning to back off.
Social Interactions
Dogs are inherently social animals and thrive on interaction with both humans and other dogs.
Understanding how they interact can provide insight into their behavior:
Play Behavior:
Play is fundamental for dogs, particularly in their early developmental stages.
Play bows, where a dog lowers its front legs while keeping its rear end up, signal a desire to play.
Hierarchy and Dominance:
While the notion of a strict ‘alpha’ has been debunked in recent years, dogs do understand social structures within their interactions, especially in multi-dog households.
The Impact of Environment
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping a dog’s behavior.
Changes in routine, moving to a new home, or the introduction of new family members can all influence how a dog behaves.
Familiarizing your dog with their environment and providing a consistent routine can lead to reduced anxiety and more stable behavior.
Training and Behavior Modification
Training is an invaluable tool in understanding and shaping dog behavior.
Positive reinforcement techniques, such as rewarding good behavior with treats or praise, can effectively encourage desirable actions.
It’s worthwhile to engage in regular training sessions not just for obedience, but also as a means of bonding with your dog.
Conclusion
Expanding your understanding of dog behavior is a rewarding journey that enhances the relationship between you and your furry companion.
By observing their body language, vocalizations, and social interactions, along with considering environmental factors, you can provide a nurturing and supportive environment for your dog.
As you learn more about their unique ways of communicating, you’ll foster mutual respect and a lasting bond that enhances the joy of having a dog in your life.