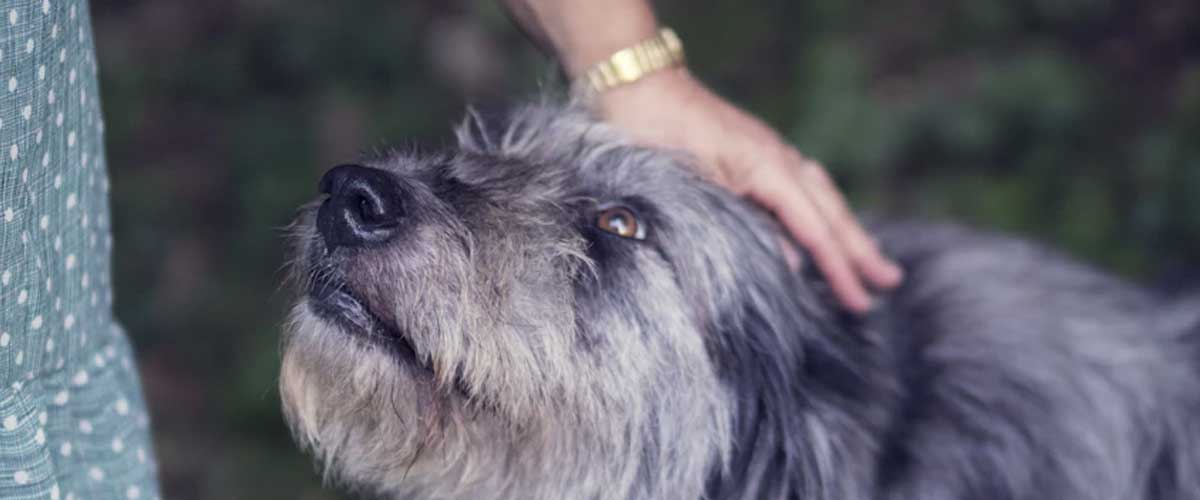
As dogs age, their needs and behaviors can change significantly, leading to a phenomenon that many pet owners may not fully understand: dog anxiety.
It’s important for dog owners to recognize that anxiety can manifest in various ways across different life stages, influenced by physical, mental, and environmental factors.
Understanding Anxiety in Dogs
Puppies and young dogs are often in a phase of rapid development where they form their initial perceptions of the world.
However, as they grow older, they might start to exhibit signs of anxiety related to separation, loud noises, or changes in their environment.
Puppy socialization is crucial during this stage, as it helps establish a foundation of confidence.
Without proper exposure to different stimuli and experiences, young dogs may become more anxious as they mature.
Evolving, Growing and Changing
As dogs transition into middle age, their anxiety can also evolve.
Physical health issues begin to develop during this stage, and pain or discomfort can exacerbate feelings of anxiety.
Conditions like arthritis can affect their ability to enjoy activities they once loved, leading to frustration and anxiety when they are unable to cope with these changes.
Additionally, cognitive decline can set in, with some dogs experiencing canine cognitive dysfunction syndrome (CDS), which is similar to dementia in humans.
This can lead to confusion, disorientation, and increased anxiety, particularly during the night, resulting in behaviors like pacing or whining.
Older Dogs and Anxiety
Older dogs often face health challenges that can contribute to heightened anxiety.
For instance, the loss of a companion, diminished physical abilities, or the stresses of a new environment can lead to increased feelings of insecurity.
Their senses, particularly sight and hearing, may start to deteriorate, making them more susceptible to startling noises or sudden movements.
This sensory decline can further complicate their interactions with the world, resulting in avoidance behaviors or fear-driven reactions.
Consistent
Another significant aspect of aging is the role that routine plays in a dog’s life.
Older dogs often thrive on predictability and consistency.
Changes in their daily routine, such as a new family member, a move, or the introduction of new animals, can trigger anxiety reactions.
They may exhibit signs such as excessive barking, chewing, or a reluctance to engage with people or other pets.
Creating a stable environment with familiar routines can help alleviate some of this anxiety.
Elderly Dog Behaviour Changes
A crucial factor that impacts dog anxiety is the bond they share with their human companions.
Dogs are social animals, and their emotional health is deeply intertwined with the relationships they have with the people around them.
As owners, it’s essential to be attuned to changes in your dog’s behavior, especially as they age.
Spending quality time, providing mental stimulation, and ensuring they feel secure can significantly reduce feelings of anxiety.
Training and Behavioural Support
Training and behavioral interventions can also play an important role in managing anxiety in aging dogs.
Positive reinforcement techniques can help reshape anxious behaviors.
Techniques such as desensitization and counter-conditioning allow dogs to gradually acclimate to stimuli that may cause anxiety.
Providing a safe space where they can retreat when feeling overwhelmed is equally important.
This could be a cozy bed in a quiet corner or a crate where they feel secure.
Anxiety Aids
Moreover, exploring the use of calming aids, such as anxiety wraps, pheromone diffusers, or calming supplements, can be beneficial for some dogs.
It is also essential for pet owners to regularly consult with veterinarians, as they can assess whether medication for anxiety is recommended or if there are underlying physical health issues contributing to anxiety.
In Summary
As dogs age, recognizing the signs and underlying causes of anxiety is vital for their well-being.
Understanding that their anxiety might stem from a combination of physical discomfort, cognitive decline, environmental changes, and social needs allows pet owners to provide better care.
By creating a supportive and understanding environment, we can help our aging dogs live happier and more comfortable lives.
The bond we share with them, characterized by love, patience, and attention, will ultimately be the most reassuring aspect of their journey through the aging process.