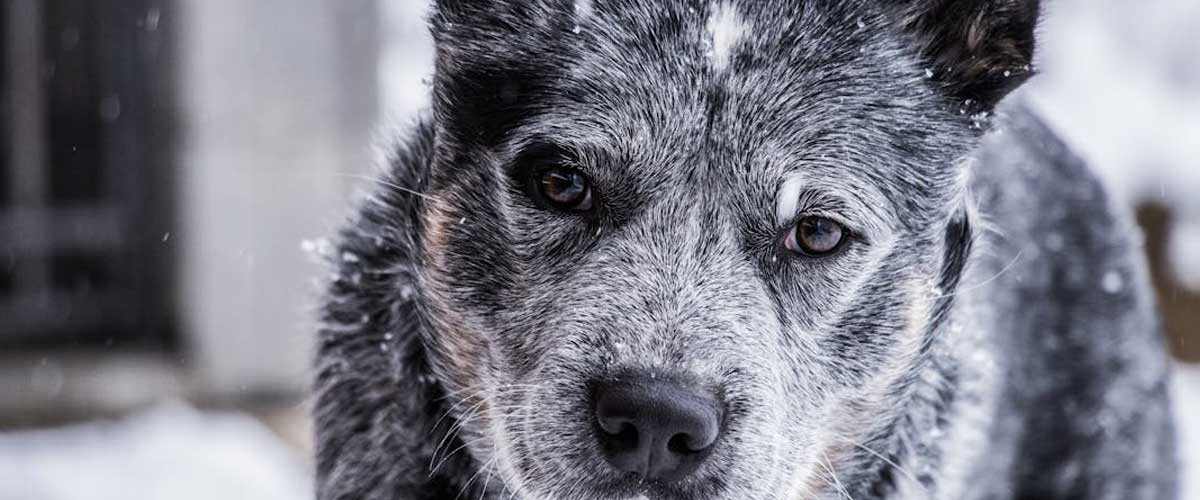
Arctic dogs, often known by their breeds such as the Alaskan Malamute, Siberian Husky, and Greenland Dog, have long been pivotal in the history and culture of the Arctic regions.
These remarkable canines have adapted to some of the harshest climates on Earth, showcasing not only their physical prowess but also their deep bond with humans in the pursuit of survival and companionship.
A Brief History
The origin of Arctic dogs can be traced back thousands of years to the indigenous peoples of the Arctic regions, including the Inuit and Sami cultures.
These dogs were bred for specific traits, including strength, endurance, and the ability to withstand extreme cold.
They served multiple roles, including pulling sleds, hunting game, and providing companionship to their human counterparts.
Physical Characteristics
Arctic dogs are known for their robust physiques and thick fur coats, which are essential adaptations to their frigid environments.
Their double coats, featuring a dense undercoat insulating them from the cold and longer guard hairs protecting against wind and moisture, allow them to thrive in temperatures that can plummet well below freezing.
Many Arctic breeds also possess larger sizes and strong limbs, which are ideal for pulling heavy sleds over snow-covered terrain.
Temperament and Training
Arctic dogs are not just physically impressive; they possess unique temperaments that make them both challenging and rewarding to train.
Generally known for their intelligence, independence, and strong prey drive, these dogs require a knowledgeable owner who can provide consistent training and a structured environment.
Socialization from a young age is crucial; these dogs flourish in families that offer regular exercise and mental stimulation.
The Role of Arctic Dogs Today
While modern technology has reduced the reliance on sled dogs for transportation and hunting, Arctic dogs continue to play important roles in contemporary life.
They are still essential in many remote areas for transportation and are celebrated in various winter sports, including dog sledding races.
Events like the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race emphasize the incredible capabilities of these dogs and serve as a testament to their historical significance.
Moreover, with their engaging personalities and striking looks, Arctic dogs have gained popularity as companions in homes around the world.
Welfare organizations advocate for their adoption and responsible ownership, reminding potential owners of the commitment required to care for such active and intelligent dogs.
Preservation and Challenges
As interest in Arctic dogs grows, so does the concern for their welfare and conservation.
Some breeds face challenges due to overbreeding and changing lifestyles, which can lead to health issues.
It’s essential for breeders and owners alike to prioritize health and genetics to preserve the unique qualities of these dogs.
Climate change also poses a significant threat to the environments that these dogs have called home for generations.
As ice melts and habitat shifts, the traditional roles of Arctic dogs may change, necessitating further adaptation and resilience.
Conclusion
Arctic dogs are more than just pets; they are a symbol of endurance, partnership, and the spirit of survival in extreme conditions.
Their legacy is intertwined with the lives of the peoples of the Arctic, and they continue to capture the hearts of many around the globe.
By understanding and appreciating these remarkable animals, we can ensure that their lineage and cultural significance remain alive for future generations.