Dogs, descendants of wolves, share a fascinating history that highlights their social structures and hunting strategies.
One of the most intriguing aspects of canine behavior is pack hunting, a strategy that has evolved over thousands of years, significantly influencing the domestication and roles of dogs in human society.
Origins of Pack Hunting
The roots of pack hunting can be traced back to the social behavior of wolves.
As highly social animals, wolves hunt in packs to increase their chances of capturing prey.
This communal approach not only enables them to take down larger animals but also improves their chances of survival in the wild.
The cooperative strategy allows them to divide labor, with each member playing a specific role, such as tracking, chasing, or ambushing.
As humans began to domesticate wolves, the traits that favored pack hunting remained prominent.
Early dog breeds were developed based on their abilities and roles in human activities, and those with strong pack-hunting instincts were particularly prized.
The Role of Dogs in Hunting
Throughout history, different cultures have harnessed the pack-hunting capabilities of dogs for various purposes.
In ancient societies, dogs helped humans hunt game for food and security.
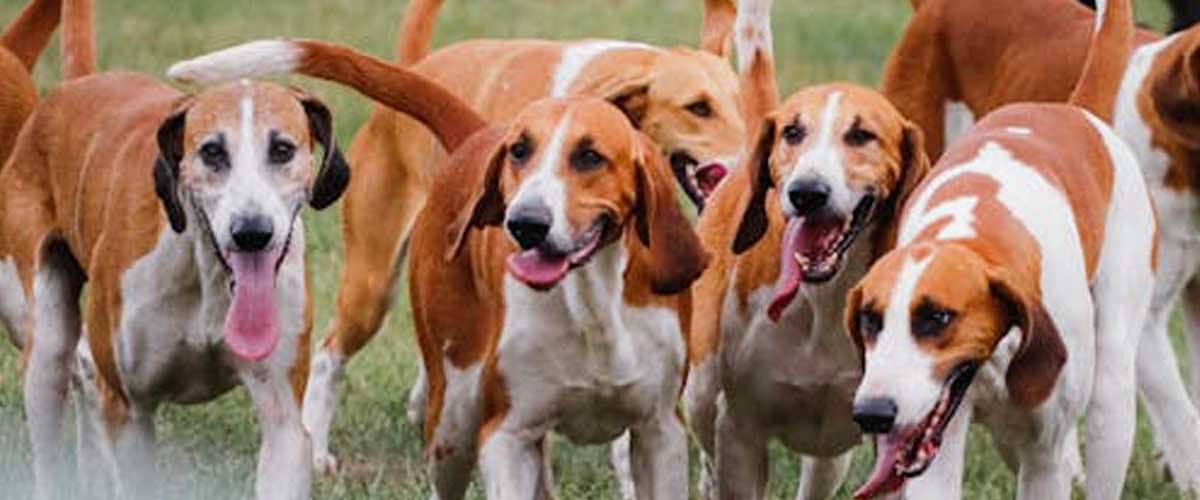
Breeds like hounds and terriers were developed to assist hunters in tracking and bringing down wild animals.
These dogs could follow scents, flush out birds, and even corner larger prey like deer or boar.
The cooperation seen in wild wolf packs mirrors the team dynamics observed in traditional dog hunting packs.
Hunt leaders, often the most skilled or experienced dogs, would lead chases, with other dogs supporting the effort, much like wolves in their natural habitats.
Humans learned to train dogs to enhance their natural instincts, resulting in sophisticated hunting partnerships that would last for generations.
Evolution of Pack Hunting Techniques
Over time, the techniques and strategies used in pack hunting by dogs have evolved.
Depending on the breed, dogs have developed specific hunting styles that complement various types of prey.
Sighthounds, for instance, rely on speed and agility to chase down swift prey, while scent hounds use their incredible sense of smell to track animals over long distances.
In addition to hunting, pack behavior has also been vital for protection and companionship.
Herding dogs, such as Border Collies, display strong pack instincts as they work alongside humans to manage livestock.
Their ability to communicate effectively with both animals and humans showcases the deep-rooted social structures that have been nurtured through centuries of domestication.
Modern Implications of Pack Hunting Today, while the primary purpose of hunting with dogs may have diminished in many regions, the principles of pack hunting still play a significant role in dog training and behavior.
Many dog sports, such as agility competitions and herding trials, incorporate elements of pack dynamics, emphasizing teamwork and coordination.
Furthermore, the understanding of pack behavior has influenced how dog owners interpret their pets’ social interactions.
Recognizing that dogs possess inherent pack instincts can enhance training programs and the overall relationship between humans and their canine companions.
Conclusion
The history of pack hunting in dogs illuminates the profound bond between humans and their furry friends.
From their wolf ancestors to modern domestic companions, dogs have retained their pack-hunting instincts, adapting to various roles in human society.
As we continue to explore these ancient behaviors, we gain greater insights into the nature of dogs, allowing us to nurture and strengthen the connection we share with them.
Understanding this rich history enhances our appreciation of these remarkable animals and the integral role they play in our lives.